
In the development of cancer treatments, the use of isotopes plays a major role, particularly in oncology.Īn example of an innovative treatment is the use of a radioactive atom, lead-212. Stable isotopes such as zinc, depleted in zinc-64, help reduce corrosion of nuclear reactor cooling equipment, while limiting the production of radioactive waste. When the nuclei of isotopes are split, they generate large quantities of energy. In fission, the Pu-239 isotope of plutonium is used, as wellĪs the U-235 isotope of uranium. In nuclear fission, the process involves the disintegration or splitting of a nucleus into smaller atomic nuclei.

To form a larger atom and thus produce more energy. In the case of fusion, it is a matter of combining two nuclei of atoms Two industrial processes have been implemented: fusion and nuclear fission. Nuclear energy, as we know it, was made possible by human intervention. They are at the heart of technological innovation. Stable isotopes are very promising in a range of applications: medicine, industry, basic research and quantum computing. The use of stable isotopes helps scientists in the study of the origin of stones, or even metals. Stable isotopes are mainly used in science, for example, for the study of the chemical composition of minerals. They each have one proton and a different number of neutrons. Hydrogen has three isotopes: H, 2H and 3H. Some examples of stable isotopes: isotopes of oxygen, hydrogen, or even nitrogen. As for carbon-14, it has 6 neutrons and 8 neutrons, which creates its instability. Let's go back to the case of carbon-12, which is stable. It is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom that guarantees this stability.
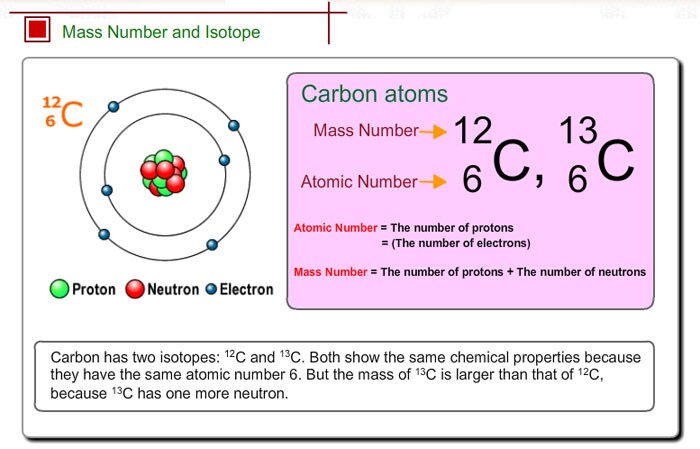
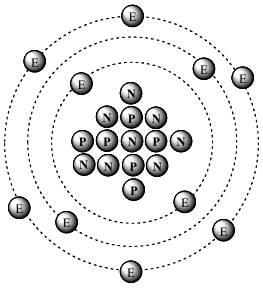
Stable isotopesStable isotopes are defined by an association between protons and neutrons. In the notation of carbon 14, we therefore write 14Ħ C, C being the chemical symbol of carbon, 14 its atomic mass number (protons + neutrons) and 6 corresponds to its atomic number, It has a total of 14 nucleons (6 protons and 8 neutrons). Because of the number of neutron they have, they have different physical properties.Ĭarbon-14 is considered an unstable isotope. However, the numberĬarbon-12 has 6 neutrons and carbon-14 has 8 neutrons. Both are isotopes of the same chemical element, carbon. Particle of neutral electric charge, which can be stable or unstable.Įach isotope of the same chemical element thus shares the same atomic number (Z), which corresponds to the number of protons they have.įrom each other by their atomic mass number (neutrons + protons) the number of neutrons they have is different.Īn example - isotopes of carbonTake the example of the isotopes of carbon: carbon-12 and carbon-14. However, isotopes, which belong to the same chemical element, are distinguished by different physical properties because of the number of neutrons they have. They belong to the same chemical element because they have the same Two atoms with the same number of protons are called isotopes. Inside the atomic nucleus, the number of protons defines the chemical properties of the atom. We distinguish a type of atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. The cumulative number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus is the atomic mass of the atom. Inside the atom's nucleus are particles called neutrons, which are bound to protons. Atoms are composed of a nucleus, around which electrons orbit. The matter that surrounds us, water, air, or even living beings, is made up of atoms, particles invisible to the naked eye. Proven expertise in recycling and nuclear waste management


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
